HashMap 哈希表
定义
- HashMap
- 用 Array + LinkedList(chaining) 实现的能在平均 O(1)时间快速增删查的数据结构
- 表内存的数据需要实现 equals()和 hashCode()
- LinkedHashMap
- 有顺序的 hashmap, 遍历顺序是 key 插入的顺序
- 所有的 key 按顺序存成一个 LinkedList
- TreeMap
- 有顺序的 map, 遍历顺序是 key 从小到大
- 所有的 key 存成一个红黑树(self-balancing binary tree)
- 增删查 O(logN)
- HashSet
- 没有 key 的 HashMap,只存一个值
When to use HashMap
当需要快速查找数据时,可以利用 HashMap 加速查找
注意要查找的数据结构实现了 equals()和 hashCode()
Array 和 HasMap 的区别在于
- Array 无法快速查找,Hashmap 可以
- Array 里的元素是有顺序的,HashMap 没有
- Array 的 overhead 比较小,HashMap 实现比较复杂
Q1 Two Sum 例题
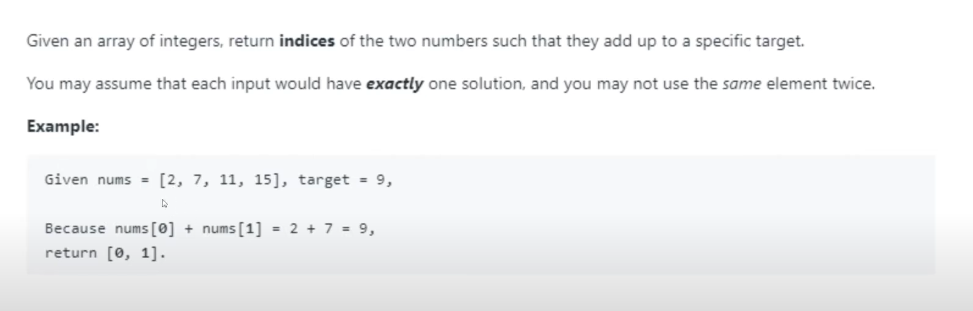
Brute Force 暴力解法
代码
时间复杂度为 O(n^2)
for x in array:
for y in array:
if index(x) != index(y) && x + y == target:
return index(x), index(y)
HashMap 解法
但需要快速查找数据时,可以利用 HashMap 加速查找
HashMap (查找时间复杂度为 O(1))
- 记录下之前见过的
{key: 值,value: index} - 对于 array 里每一个数 x, 如果 map 里存在 target-x,那就找到了答案
High Level Idea
查找对象: 目前见到的值 -> index
解决步骤
- Initialize HashMap
- For each number x in array
- if target - x exists in array, return their indices
- Put
{x, index(x)}
复杂度
- 时间 O(n)
- 空间 O(n)
代码
时间复杂度为 O(n)
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Interger> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(map.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {
return new int[]{map.get(target - nums[i]), i};
}
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
return new int[2];
}
Two pointers 解法
要求: 如果 返回值 value 而不是返回 index 的话。
High Level Idea
- Two Pointers
(array needs to be sorted), Opposite direction
sort: O(nlogN)

- Each iteration we will have a sum of two pointers -> array[i] + array[j]
- case 1: array[i] + array[j] = target -> we found the answer
- case 2: array[i] + array[j] > target -> too big, move the right pointer left
- case 3: array[i] + array[j] < target -> too small, move the left pointer right
- Sort the input array
- Initialize two pointers i = 0 and j = n - 1
- While i < j
- arr[i] + arr[j] == target -> return
- arr[i] + arr[j] > target -> j--
- arr[i] + arr[j] < target -> i++
代码
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int i = 0, j = nums.length - 1;
while (i < j) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[j];
if (sum == target) {
return new int{nums[i], nums[j]};
} else if (sum > target) {
j--;
} else {
i++;
}
}
return null;
}
Q560 Subarray Sum Equals K 例题


High Level Idea
当需要快速查找数据时,可以利用 HashMap 加速查找
查找对象: all sum seen so far until current index -> #number of times it occurs
当 current sum - k 存在于 map 内,那么 answer += map.get(sum-k)
因为 sum - k 存在于 map 内说明之前 sum(0, x) = k 多出现了 y 次:
subarray sum = current sum - sum(0, x) = k 多出现了 y 次
要点:Map 内一开始存在一个1, 代表 sum = 0 默认出现一次
Solution Steps:
- Initialize HashMap with 1
- Initialize sum = 0, result = 0
- For each number x in array
- sum += x
- if sum - k is in the map -> result += map.get(sum -k)
- put sum into the map, increase its count if exists
代码
public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); // <总和, 出现次数>
map.put(0, 1);
int sum = 0, count = 0;
for (int x : nums) {
sum += x;
if (map.containsKey(sum - k)) {
count += map.get(sum - k);
}
map.puth(sum, map.getOrDefault(sum, 0) + 1);
}
return count;
}
更多例题
- Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters (3)
- Group Anagrams (49)
- Copy List with Random Pointer (138)
- Longest Substring with At Most K Distinct Characters (340)
- Brick Wall (554)
- Encode and Decode TinyURL (535)
来源
- 哈希表 HashMap 解题套路【LeetCode 刷题套路教程 7】: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UtX1BPPjojc&list=PLV5qT67glKSErHD66rKTfqerMYz9OaTOs&index=7