SQLModel 学习
SQLModel is a library for interacting with SQL databases from Python code, with Python objects. It is designed to be intuitive, easy to use, highly compatible, and robust.
SQLModel is based on Python type annotations, and powered by Pydantic and SQLAlchemy.
key features
- Intuitive to write: Great editor support. Completion everywhere. Less time debugging. Designed to be easy to use and learn. Less time reading docs.
- Easy to use: It has sensible defaults and does a lot of work underneath to simplify the code you write.
- Compatible: It is designed to be compatible with FastAPI, Pydantic, and SQLAlchemy.
- Extensible: You have all the power of SQLAlchemy and Pydantic underneath.
- Short: Minimize code duplication. A single type annotation does a lot of work. No need to duplicate models in SQLAlchemy and Pydantic.
Example
Database table
| id | name | secret_name | age |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Deadpond | Dive Wilson | null |
| 2 | Spider-Boy | Pedro Parqueador | null |
| 3 | Rusty-Man | Tommy Sharp | 48 |
Create a SQLModel Model
from typing import Optional
from sqlmodel import Field, SQLModel
class Hero(SQLModel, table=True):
id: Optional[int] = Field(default=None, primary_key=True)
name: str
secret_name: str
age: Optional[int] = None
That class Hero is a SQLModel model, the equivalent of a SQL table in Python code.
And each of those class attributes is equivalent to each table column.
Create Rows
hero_1 = Hero(name="Deadpond", secret_name="Dive Wilson")
hero_2 = Hero(name="Spider-Boy", secret_name="Pedro Parqueador")
hero_3 = Hero(name="Rusty-Man", secret_name="Tommy Sharp", age=48)
This way, you can use conventional Python code with classes and instances that represent tables and rows, and that way communicate with the SQL database.
Write to the Database
# Create a SQLModel Model...
# Create Rows...
engine = create_engine("sqlite:///database.db") # 创建数据库连接引擎的方式
SQLModel.metadata.create_all(engine) # 自动搜索所有 SQLModel 类,并创建未被创建的 table
with Session(engine) as session:
# 加入 rows
session.add(hero_1)
session.add(hero_2)
session.add(hero_3)
# 提交修改
session.commit()
Select from the Database
# Create a SQLModel Model...
engine = create_engine("sqlite:///database.db")
with Session(engine) as session:
statement = select(Hero).where(Hero.name == "Spider-Boy")
hero = session.exec(statement).first()
print(hero)
Relationships-One-to-Many
Define Relationships Attributes
hero table
| id | name | secret_name | age | team_id |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Deadpond | Dive Wilson | null | 2 |
| 2 | Spider-Boy | Pedro Parqueador | null | 1 |
| 3 | Rusty-Man | Tommy Sharp | 48 | 1 |
team table
| id | name | headquarters |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Preventers | Sharp Tower |
| 2 | Z-Force | Sister Margaret's Bar |
Declare Relationship Attributes
Update table structure
from sqlmodel import Field, Session, SQLModel, create_engine
class Team(SQLModel, table=True):
id: int | None = Field(default=None, primary_key=True)
name: str = Field(index=True)
headquarters: str
class Hero(SQLModel, table=True):
id: int | None = Field(default=None, primary_key=True)
name: str = Field(index=True)
secret_name: str
age: int | None = Field(default=None, index=True)
# Add a field in
team_id: int | None = Field(default=None, foreign_key="team.id")
# Code below omitted 👇
Add Relationship in two SQLModel
from sqlmodel import Field, Relationship, Session, SQLModel, create_engine
class Team(SQLModel, table=True):
id: int | None = Field(default=None, primary_key=True)
name: str = Field(index=True)
headquarters: str
# Add new relationship
heroes: list["Hero"] = Relationship(back_populates="team")
class Hero(SQLModel, table=True):
id: int | None = Field(default=None, primary_key=True)
name: str = Field(index=True)
secret_name: str
age: int | None = Field(default=None, index=True)
team_id: int | None = Field(default=None, foreign_key="team.id")
# Add new relationship
team: Team | None = Relationship(back_populates="heroes")
# Code below omitted 👇
Relationships-Many-to-Many
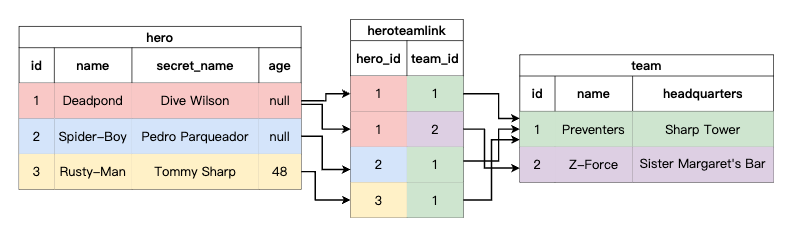
Create Link Table Model
from sqlmodel import Field, Relationship, Session, SQLModel, create_engine
class HeroTeamLink(SQLModel, table=True):
team_id: int | None = Field(default=None, foreign_key="team.id", primary_key=True)
hero_id: int | None = Field(default=None, foreign_key="hero.id", primary_key=True)
# Code below omitted 👇
Team Model
# Code above omitted 👆
class Team(SQLModel, table=True):
id: int | None = Field(default=None, primary_key=True)
name: str = Field(index=True)
headquarters: str
heroes: list["Hero"] = Relationship(back_populates="teams", link_model=HeroTeamLink)
# Code below omitted 👇
Hero Model
# Code above omitted 👆
class Hero(SQLModel, table=True):
id: int | None = Field(default=None, primary_key=True)
name: str = Field(index=True)
secret_name: str
age: int | None = Field(default=None, index=True)
teams: list[Team] = Relationship(back_populates="heroes", link_model=HeroTeamLink)
# Code below omitted 👇
Resource
- SQLModel official doc: https://sqlmodel.tiangolo.com/