PyTorch
What is PyTorch ?
- An open source machine learning framework.
- A Python package that provides two high-level features:
- Tensor computation (like NumPy) with strong GPU acceleration
- Deep neural networks builts on a tape-based autograd system (calculate gradient)
PyTorch vs TensorFlow
| PyTorch | TensorFlow | |
|---|---|---|
| Developer | Facebook AI | Google Brain |
| Interface | Python & C++ | Python, C++, JavaScript, Swift |
| Debug | Easier | Difficult (easier in 2.0) |
| Application | Research | Production |
Tensor unit
- High-dimensional matrix(array)
Data type
| Data Type | dtype | tensor |
|---|---|---|
| 32-bit floating point | torch.float32 | torch.FloatTensor |
| 64-bit integer (signed) | torch.int64 | torch.LongTensor |
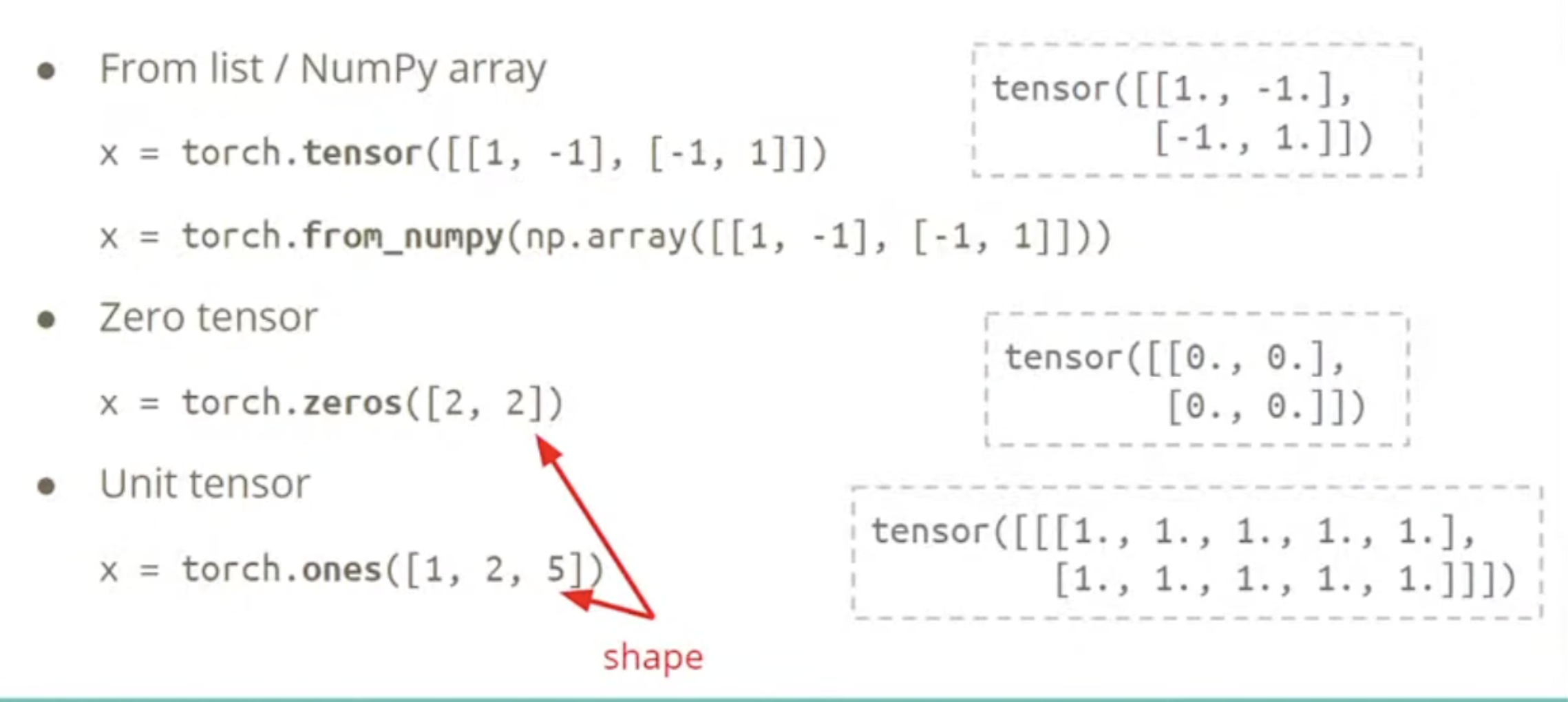
Shape of Tensors

Constructor
Operator
Squeeze

Unsqueeze

Transpose

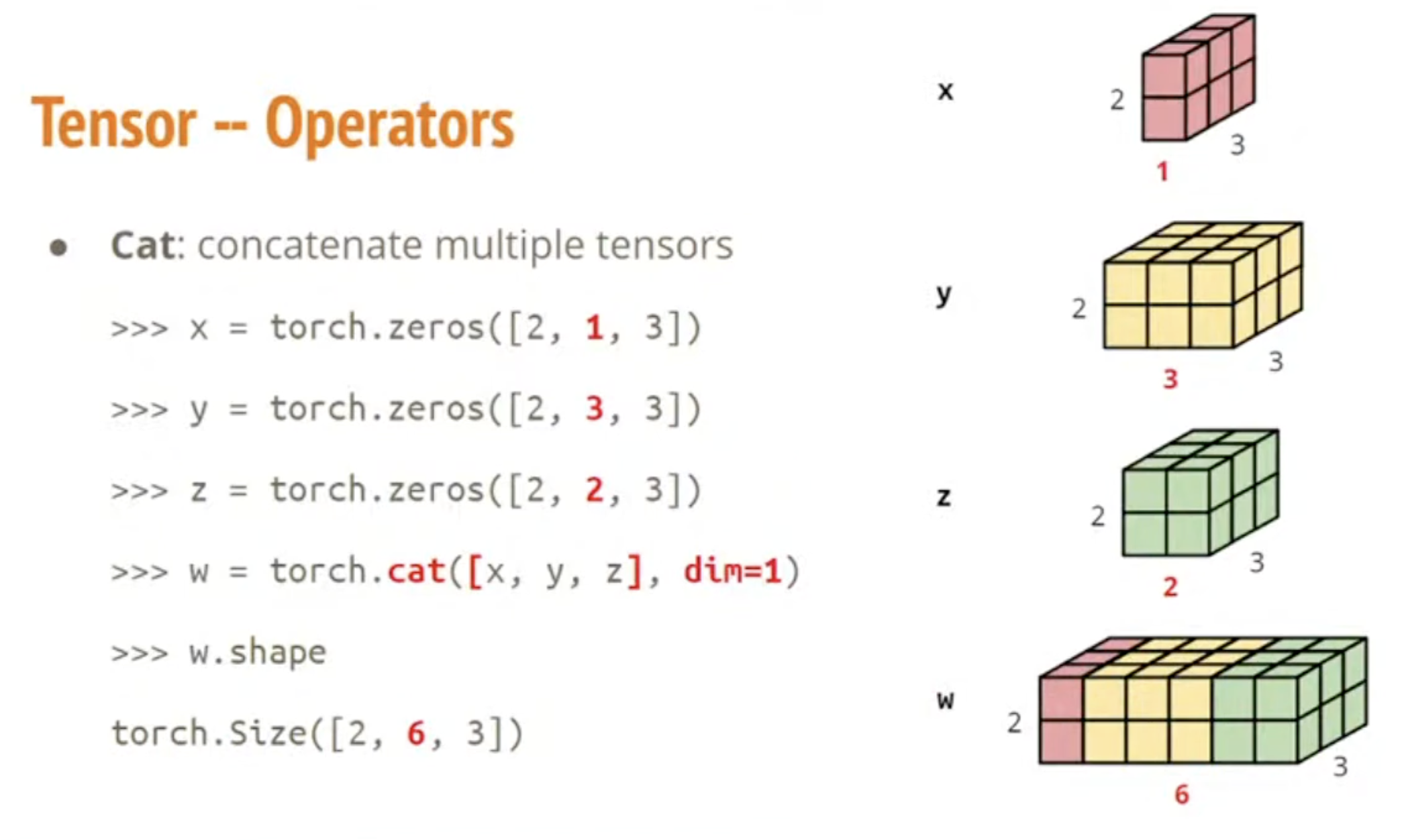
Concatenate
Others
- Addition:
- Subtraction:
- Power:
- Summation:
- Mean:
PyTorch vs NumPy
Attributes
| PyTorch | NumPy |
|---|---|
| x.shape | x.shape |
| x.dtype | x.dtype |
Shape manipulation
| PyTorch | NumPy |
|---|---|
| x.reshape / x.view | x.reshape |
| x.squeeze() | x.squeeze() |
| x.unsqueeze(1) | np.expand_dims(x, 1) |
Device
-
Default: tensors & modules will be computed with CPU
-
CPU:
x = x.to("cpu") -
GPU:
x = x.to("cuda") -
Check if your computer has NVIDIA GPU:
torch.cuda.is_available() -
Multiple GPUs: specify
cuda:0,cuda:1,cuda:2, ...
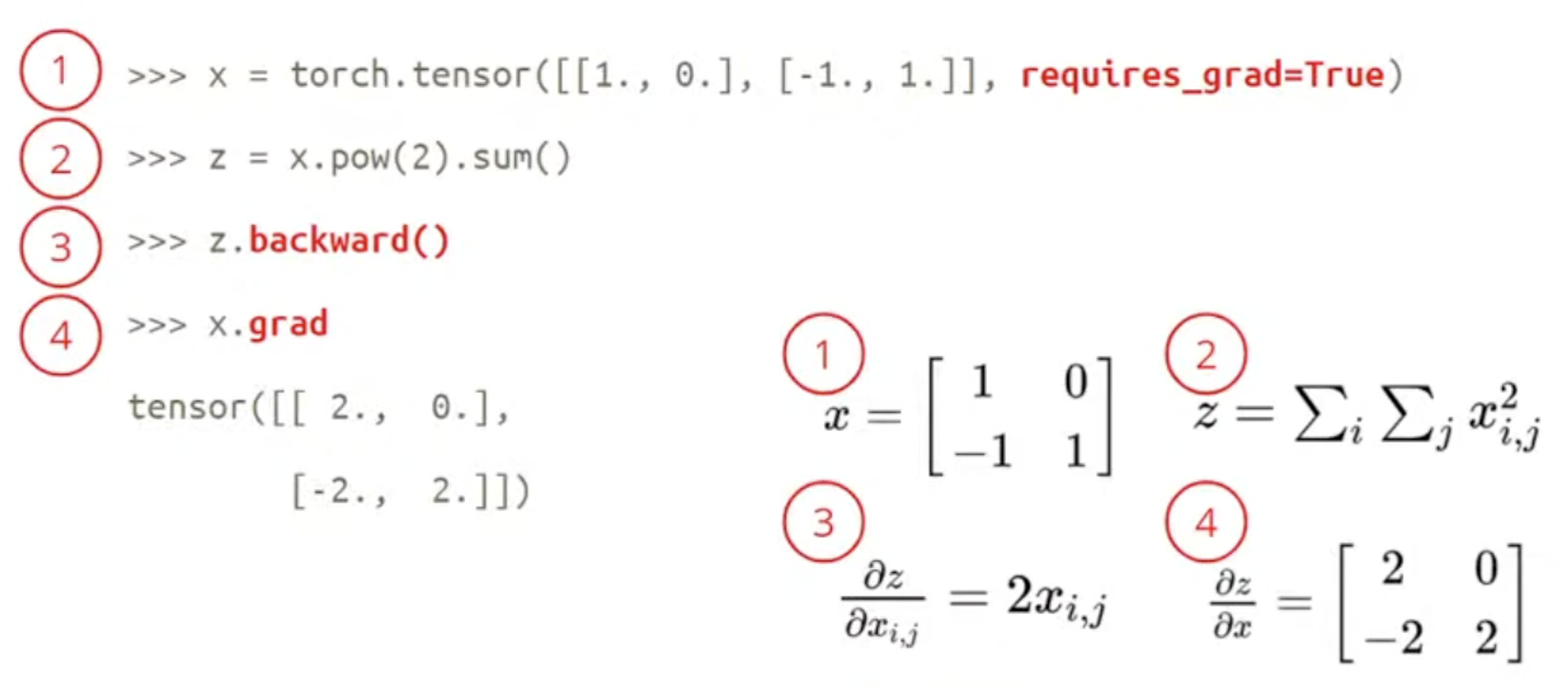
How to calculate Gradient ?
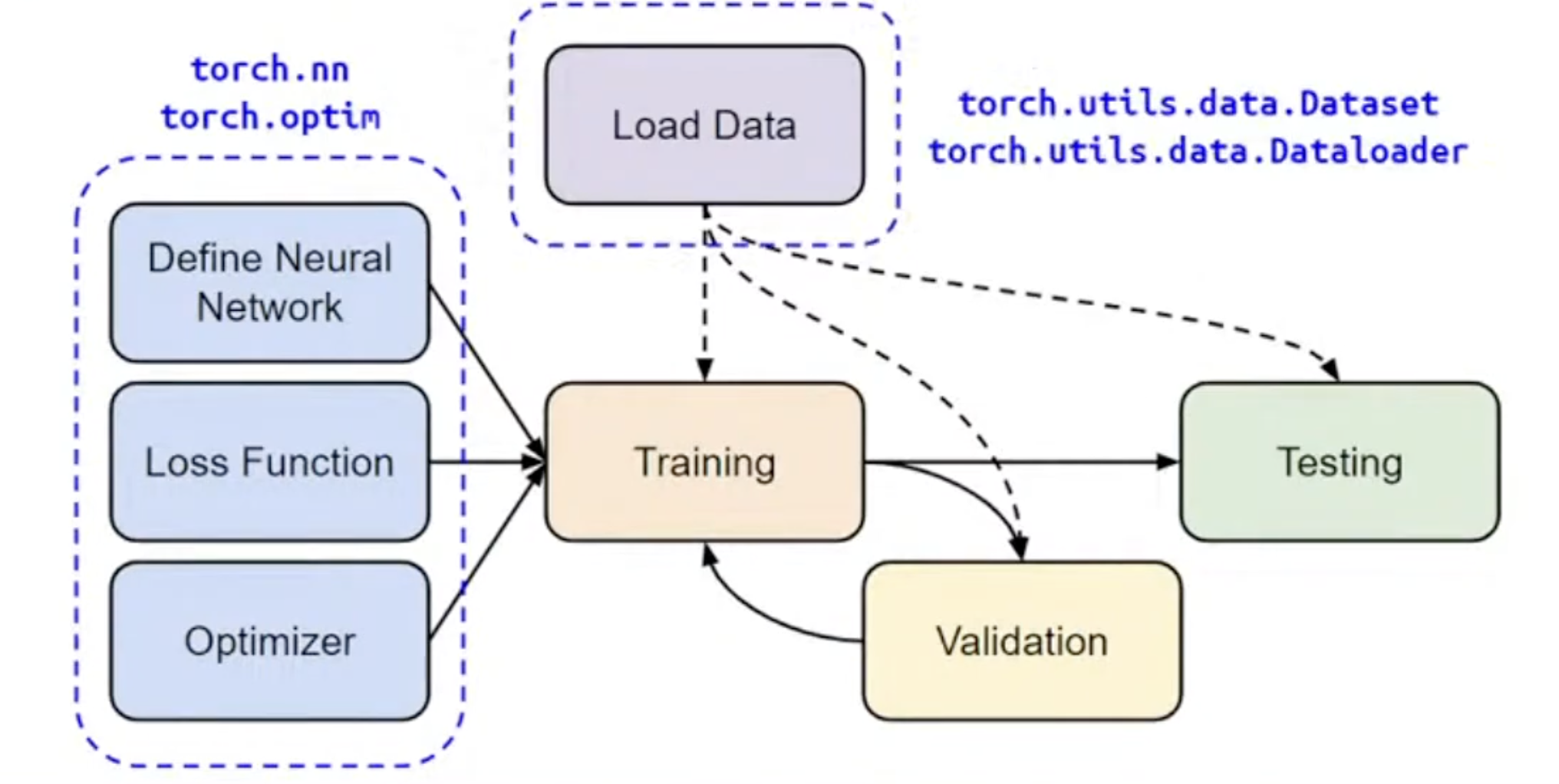
Overview of the DNN Training Procedure
Dataset & Dataloader
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
class MyDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, file):
self.data = ... # Read data & preprocess
def __getitem__(self, index):
return self.data[index] # Returns one sample at a time
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data) # Returns the size of the dataset
dataset = MyDataset(file)
# Training: shuffle=True
# Testing: shuffle=False
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_szie, shuffle=True)
torch.nn
Neural Network Layers
- Linear Layer (Fully-connected Layer)
torch.nn.leanear(in_features, out_features)
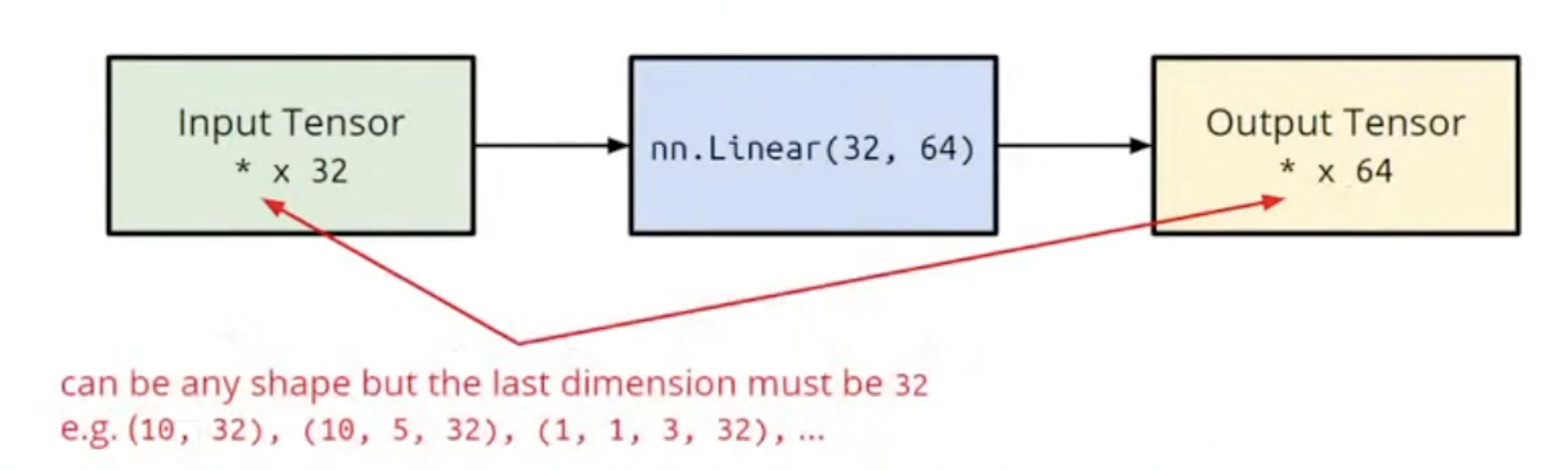

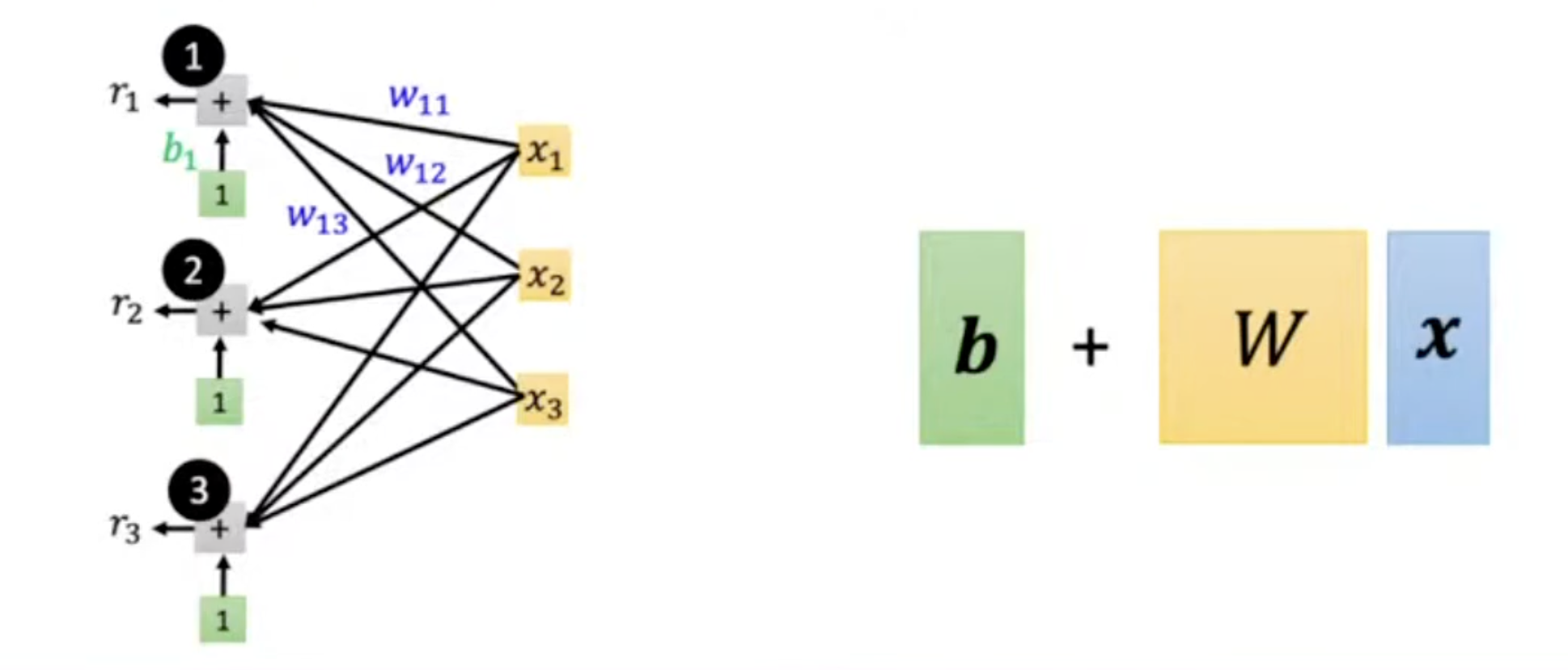
layer = torch.nn.Linear(32, 64)
layer.weight.shape # torch.Size([64, 32])
layer.bias.shape # torch.Size([64])
Activation Functions
- Sigmoid Activation:
nn.Sigomid() - ReLU Activation:
nn.ReLU()
Loss Functions
- Mean Squared Error (for linear regression):
nn.MSELoss() - Cross Entropy (for classification):
nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
Build your own neural network
import torch.nn as nn
class MyModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self): # Initialize your model & define lyaers
super(MyModel, self).__init__()
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(10, 32), # 第一层全连接层
nn.Sigmoid(), # 激活函数
nn.Linear(32, 1) # 第二层全连接层(输出层) 5)
)
def forword(self, x): # Compute output of your NN
return self.net(x)
-
输入维度:10
输入数据是一个 10 维的特征向量(或批量数据形状为[batch_size, 10])。 -
第一层
nn.Linear(10, 32)- 全连接层(线性层),将输入从 10 维映射到 32 维。
- 参数数量:权重矩阵
W的形状为[32, 10],偏置b的形状为[32],共32*10 + 32 = 352个可训练参数。
-
激活函数
nn.Sigmoid()- 对第一层的输出逐元素应用 Sigmoid 函数(),将值压缩到
(0, 1)区间。 - 引入非线性,使网络能够学习复杂模式。
- 对第一层的输出逐元素应用 Sigmoid 函数(),将值压缩到
-
第二层
nn.Linear(32, 1)- 输出层,将 32 维特征映射到 1 维输出(如回归任务的标量值或二分类的 logit)。
- 参数数量:权重
W的形状为[1, 32],偏置b的形状为[1],共1*32 + 1 = 33个参数。

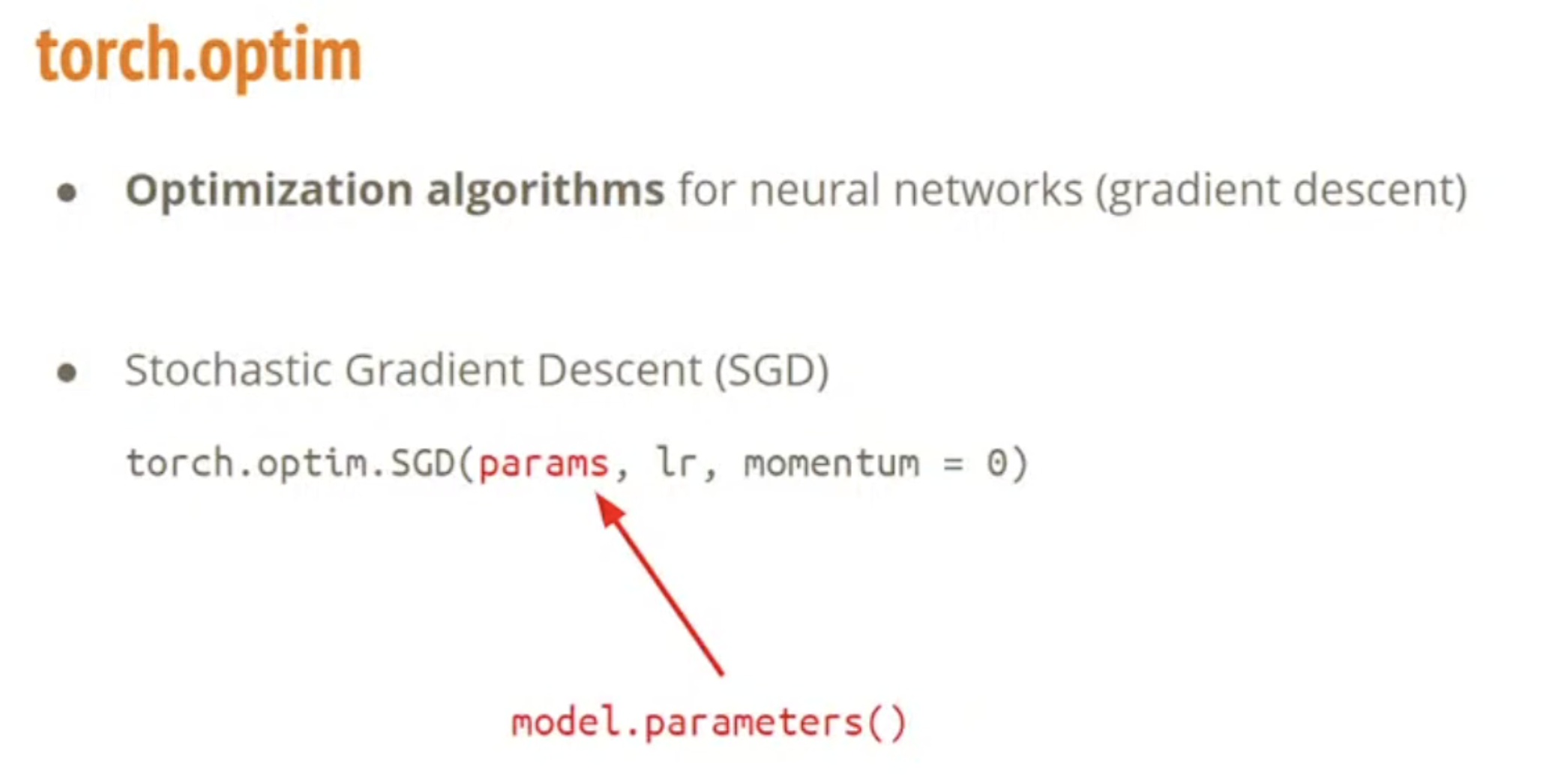
Optimizer
Neural Network Training
Preparation
dataset = MyDataset(file) # read data via MyDataset
batch_size = 16
train_set = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size, shuffle=True) # Put dataset into Dataloader
device = "cuda"
model = MyModel().to(device) # Contruct model and move to device (cpu/cuda)
criterion = nn.MSELoss() # Set loss function
learning_rate = 0.1
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), learning_rate) # Set optimizer
Training (Training Set)
n_epochs = 2
for epoch in range(n_epochs): # Iterate n_epochs
model.train() # Set model to train mode
for x, y in train_set: # iterate through the dataloader
optimizer.zero_grad() # Set gradient to zero
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device) # Move data to device (cpu/cuda)
pred = model(x) # Forward pass (compute output)
loss = criterion(pred, y) # Compute loss
loss.backword() # Compute gradient (backpropagation)
optimizer.step() # Update model with optimizer
Evaluation (Validation Set)
model.eval() # Set model to evaluation mode
total_loss = 0
for x, y in dv_set: # Iterate through the dataloader
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device) # Move data to device (cpu/cuda)
with torch.no_grad(): # Disable gradient calculation
pred = model(x) # Forward pass (compute output)
loss = criterion(pred, y) # Compute loss
total_loss += loss.cpu().item() * len(x) # Accumulate loss
avg_loss = total_loss / len(dv_set.dataset) # Compute averaged loss
这些 loss 将决定要不要最终把模型存下来,取决 model 是否进步。
Evaluation (Testing Set)
model.eval() # Set model to evaluation mode
preds = []
for x in tt_set: # Iterate through the dataloader
x = x.to(device) # Move data to device (cpu/cuda)
with torch.no_grad(): # Disable gradient calculation
pred = model(x) # Forward pass (compute output)
preds.append(pred.cpu()) # Collect prediction
Save/Load a Neural Network
Save
torch.save(model.state_dict(), path)
Load
checkpoint = torch.load(path)
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint)
More About PyTorch
- torchaudio: speech/audio processsing
- torchtext: natural language processing
- torchvision: computer vision
- skorch: scikit-learn + pyTorch
- Useful github repositories using PyTorch
- Huggingface Transformers (transformer models: BERT, GPT, ...)
- Fairseq (sequence modeling for NLP & speech)
- ESPnet (speech recognition, translation, synthesis, ...)
- Many implementation of parpers
- ...
Reference
PyTorch & Related Resources
- PyTorch Official Website
- PyTorch GitHub Repository
- PyTorch for NumPy Users (GitHub)
- PyTorch vs. TensorFlow: What You Need to Know (Udacity Blog)